yo ants,
DTC 311 - Thermactor air system inoperable. "...The computer determined that for some reason the fresh air injection from the Thermactor system was not present. There are several components that make up this system. The initial component is the smog pump. The first checks I would make are the hoses and plumbing from the smog pump back to the diverter valve (behind the pass. cylinder head) and then on to the crossover pipe at the back of the heads and down to the catalytic converter. The check valves that are at the center of the cross over pipe and the top of the metal tube from the cat are often the culprits as they can and do snap in half as the get old. If the plumbing looks to be in good order we can discuss the slightly more complicated aspects of the system. The diverter valve also has two vacuum lines running to it. Make certain they are in place and intact. (Computer needs to be able to control the flow of fresh air by the Thermactor system)..."
DTC 311, "...KC1 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 311: VISUALLY INSPECT VACUUM HOSES
Vacuum hoses damaged.
AIRB/AIRD valve inoperative.
Air Pump inoperative.
AIRB/AIRD solenoids damaged.
miesk5 Note; as I mentioned in another thread here; In place of the breakout box, go to the EEC pin instead; to help see, EEC Connector Pin Diagram
Source: by Fireguy50 (Ryan M) at
http://web.archive.org/web/20131229163930/http://oldfuelinjection.com/images/eec04.gif
EEC Connector Pin LEGEND Bronco & Ford Truck & Van: 4.9, 460, 5.0, 5.8; Source: by Ryan M (Fireguy50) at
http://web.archive.org/web/20131029020805/http://oldfuelinjection.com/truckpinouts.html
****DO THIS FIRST:
KC10 MEASURE AIRB/AIRD SOLENOID RESISTANCE
Key off.
Disconnect both AIRB/AIRD solenoid connectors and measure both solenoid resistances.
Is each resistance between 50 and 100 ohms? if Yes, they are good electrically. ****
DTCs 311 indicates the Secondary Air Injection system is inoperative
Possible causes:
Visually inspect vacuum lines for disconnects in the AIR system.
Visually inspect for proper vacuum line routing. Refer to VECI decal.
Visually inspect Air Pump for broken or loose Air Pump Belt. Refer to Section 13A for adjustment/replacement.
Were any problems found?
Yes SERVICE as necessary. RERUN Quick Test.
NO GO to KC2
KC2 CHECK AIR VACUUM LINES
Carefully check AIR vacuum lines; From AIRB solenoid to AIRB valve.
From AIRD solenoid to AIRD valve.
From Manifold Vacuum TREE to AIRB/AIRD solenoids.
Check for obstructions, cracks, kinks, and leaks, etc.
Are vacuum lines in good condition?
Yes SERVICE as necessary. RERUN Quick Test.
NO Go to KC 5
KC5 CHECK AIRB AND AIRD SOLENOIDS ELECTRICAL OPERATION
DVOM on 20 volt scale.
Enter Output State Diagnostic Test Mode (DTM). Refer to Section 5A , Quick Test Appendix.
Disconnect AIRB solenoid.
Connect DVOM positive test lead to VPWR circuit and negative test lead to AIRB circuit of AIRB vehicle harness connector.
While observing DVOM, depress and release the throttle several times (to cycle output On and Off).
Repeat for the AIRD solenoid.
Does each solenoid circuit cycle 0.5 volt or greater?
Yes GO to KC6.
NO REMOVE jumper GO to KC10 .
KC6 CHECK AIRB/AIRD SOLENOIDS FOR INTERNAL VACUUM LEAKS
Remain in output state DTM.
Reconnect AIRD/AIRB harness connector.
Vacuum pump connected to the supply port and vacuum gauge connected to the output port of one solenoid.
Apply 15 in-Hg (51 kPa) vacuum and observe gauge.
Repeat steps above for the other solenoid.
Does vacuum gauge reading hold for each solenoid?
Yes GO to KC7
No REPLACE AIRB/AIRD solenoid assembly. RERUN Quick Test.
KC7 CHECK AIRB/AIRD SOLENOIDS FOR VACUUM CYCLING
Continue in output state DTM.
Install vacuum pump to the AIRB solenoid vacuum supply port and install a vacuum gauge to the AIRB output port.
Apply 15 in-Hg vacuum.
While cycling outputs On and Off (by depressing and releasing throttle), observe the vacuum gauge at the output.
Note: Re-apply vacuum between cycles.
Repeat for AIRD solenoid. Connect vacuum pump to the AIRD solenoid vacuum supply port and connect a vacuum gauge to the AIRD output port.
Cycle output on and off.
Does each solenoid cycle vacuum output on and off?
Yes EXIT Output State DTM, RECONNECT vacuum hoses
NO REPLACE AIRB/AIRD solenoid assembly. RERUN Quick Test.
KC10 MEASURE AIRB/AIRD SOLENOID RESISTANCE
Key off.
Disconnect both AIRB/AIRD solenoid connectors and measure both solenoid resistances.
Is each resistance between 50 and 100 ohms?
Yes GO to KC11
NO REPLACE AIRB/AIRD solenoid assembly. RECONNECT both solenoids. RERUN Quick Test.
KC11 CHECK CIRCUIT CONTINUITY
Key off.
Disconnect Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Inspect for damaged or pushed out pins, corrosion, loose wires, etc. Service as necessary.
Install breakout box, leave PCM disconnected.
Measure resistance between AIRB circuit at breakout box and AIRB circuit at vehicle harness connector.
Measure resistance between AIRD circuit at the breakout box and AIRD circuit at vehicle harness connector.
Is each resistance less than 5.0 ohms?
Yes GO to KC12
NO SERVICE open harness circuit. REMOVE breakout box. RECONNECT PCM and both solenoids. RERUN Quick Test
KC12 CHECK FOR SHORT TO GROUND
Key off.
Breakout box installed, PCM disconnected.
Disconnect both AIRB/AIRD solenoids.
Measure resistance between AIRB circuit at the breakout box and Test Pins 40, 46 and 60. Measure resistance between AIRD circuit at the breakout box and Test Pins 40, 46 and 60 at the breakout box.
Is each resistance greater than 10,000 ohms?
Yes GO to KC13 .
NO SERVICE short to ground. REMOVE breakout box. RECONNECT PCM and AIRB/AIRD solenoids. RERUN Quick Test
KC13 CHECK FOR SHORT TO POWER
Key off.
Breakout box installed, PCM disconnected.
Both AIRB/AIRD solenoids disconnected.
Measure resistance between AIRB circuit at the breakout box and Test Pins 37 and 57. Measure resistance between AIRD circuit at the breakout box and Test Pins 37 and 57 at the breakout box.
Is each resistance greater than 10,000 ohms?
Yes REPLACE PCM. REMOVE breakout box. RECONNECT both solenoids. RERUN Quick Test.
NO SERVICE short to power. REMOVE breakout box. RECONNECT PCM and AIRB/AIRD solenoids. RERUN Quick Test. If DTC is present, REPLACE PCM.
******
Thermactor Air Diverter Solenoid (aka Air Control Valve or TAD, AIRD, AM2); "...is controlled by the EEC-IV computer and provides vacuum to the Air Bypass/Air Control Valve. With vacuum present, air flows to the exhaust manifold. With no vacuum, air flows from the air pump to the catalyst..."
Source: by Ted F
Air Control Valve Functional Test; "...1.Run the engine to normal operating temperature, then increase the speed to 1500 rpm. 2.Disconnect the air supply hose at the valve inlet and verify that there is airflow present. 3.Reconnect the air supply hose. 4.Disconnect both air supply hoses. 5.Disconnect the vacuum hose from the valve. 6.With the engine running at 1,500 rpm, airflow should be felt and heard at the outlet on the side of the valve, with no airflow heard or felt at the outlet opposite the vacuum ******. 7.Shut off the engine. 8.Using a spare piece of vacuum hose, connect direct manifold vacuum to the valve's vacuum fitting. Airflow should be heard and felt at the outlet opposite the vacuum ******, and no airflow should be present at the other outlet. 9.If the valve is not functioning properly, replace it..."
---------------
Thermactor Air Bypass Solenoid (TAB, AIRB, AM1); "...is controlled by the EEC-IV computer and provides vacuum to the Air Bypass/Air Control Valve. With vacuum present, air flows through the secondary air injection system. With no vacuum, the air from the air pump is dumped to the atmosphere. Essentially, this turns the secondary air injection system on or off. The secondary air injection system adds air to the catalytic converter to improve the burning of NOx gases. This reduces emissions..."
Source: by Ted F
============
Thermactor Air Bypass/Air Control Valve; "...based on vacuum input from the Thermactor Air Bypass Solenoid, and the Thermactor Air Diverter Solenoid, this valve controls the flow of air from the air pump to the exhaust manifold and the catalyst..."
Source: by Ted F
Normally Closed Air Bypass Valve Functional Test; "...1.Disconnect the air supply hose at the valve.2.Run the engine to normal operating temperature.3.Disconnect the vacuum line and make sure vacuum is present. If no vacuum is present, remove or bypass any restrictors or delay valves in the vacuum line. 4.Run the engine at 1500 rpm with the vacuum line connected. Air pump supply air should be heard and felt at the valve outlet.5.With the engine still at 1500 rpm, disconnect the vacuum line. Air at the outlet should shut off or dramatically decrease. Air pump supply air should now be felt or heard at the silencer ports.6.If the valve doesn't pass each of these tests, replace it...."
Normally Open Air Bypass Valve Functional Test; "...1.Disconnect the air supply hose at the valve. 2.Run the engine to normal operating temperature. 3.Disconnect the vacuum lines from the valve. 4.Run the engine at 1500 rpm with the vacuum lines disconnected. Air pump supply air should be heard and felt at the valve outlet. 5.Shut off the engine. Using a spare length of vacuum hose, connect the vacuum ****** of the valve to direct manifold vacuum. 6.Run the engine at 1500 rpm. Air at the outlet should shut off or dramatically decrease. Air pump supply air should now be felt or heard at the silencer ports. 7.With the engine still in this mode, cap the vacuum vent. Accelerate the engine to 2,000 rpm and suddenly release the throttle. A momentary interruption of air pump supply air should be felt at the valve outlet. 8.If the valve doesn't pass each of these tests, replace it. Reconnect all lines..."
==========
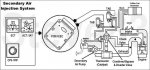
The thermactor air injection system reduces the hydrocarbon and carbon monoxide content of the exhaust gases by continuing the combustion of unburned gases after they leave the combustion chamber. This is done by injecting fresh air into the hot exhaust stream leaving the exhaust ports or into the catalyst. At this point, the fresh air mixes with hot exhaust gases to promote further oxidation of both the hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide, thereby reducing their concentration and converting some of them into harmless carbon dioxide and water.
All vehicles with 5.0L and 5.8L engines are equipped with a managed air thermactor system. This system is utilized in electronic control systems to divert thermactor air either upstream to the exhaust manifold check valve or downstream to the rear section check valve and dual bed catalyst. The system will also dump thermactor air to atmosphere during some operating modes.
The thermactor air injection system consists of the air supply pump, air bypass valve, check valves, air supply control valve, combination air bypass/air control valve, solenoid vacuum valve, thermactor idle vacuum valve and vacuum control valve. Components will vary according to year and application.
The air supply pump is a belt-driven, positive displacement, vane-type pump that provides air for the thermactor system. It is available in 19 and 22 cu. in. sizes, either of which may be driven with different pulley ratios for different applications. The pump receives air from a remote silencer filter on the rear side of the engine air cleaner attached to the pump's air inlet ****** or through an impeller-type centrifugal filter fan.
The air bypass valve supplies air to the exhaust system with medium and high applied vacuum signals when the engine is at normal operating temperature. With low or no vacuum applied, the pumped air is dumped through the silencer ports of the valve or through the dump port
The air check valve is a 1-way valve that allows thermactor air to pass into the exhaust system while preventing exhaust gases from passing in the opposite direction.
The air supply control valve directs air pump output to the exhaust manifold or downstream to the catalyst system depending upon the engine control strategy. It may also be used to dump air to the air cleaner or dump silencer.
Combination Air Bypass/Air Control Valve
The combination air control/bypass valve combines the secondary air bypass and air control functions. The valve is located in the air supply line between the air pump and the upstream/downstream air supply check valves.
The air bypass portion controls the flow of thermactor air to the exhaust system or allows thermactor air to be bypassed to atmosphere. When air is not being bypassed, the air control portion of the valve