yo 51504broncos,
DTC P0135, P0141, P0155 AND P0161: HO2S HEATER SIGNAL CIRCUIT IS OPEN, SHORTED TO GROUND, SHORTED TO B+ OR EXCESSIVE CURRENT DRAW; Possible Causes & Troubleshooting; "...DTC/HO2S Reference List: DTC P0135 = HO2S HTR-11; DTC P0141 = HO2S HTR-12; DTC P0155 = HO2S HTR-21; DTC P0161 = HO2S HTR-22.
Possible causes:
Shorts to B+ in harness or HO2S.
Water in connectors.
Cut or pulled wires.
Disconnected wiring.
Open VPWR circuit.
Open GND circuit.
Low battery voltage.
Corrosion or poor mating terminals.
Damaged PCM.
Visually inspect the HO2S circuit for exposed wiring, contamination, corrosion and proper assembly. NOTE: On some applications, a vehicle hoist may be required to access the HO2S harness. Were any concerns found during the visual inspection?
Yes, REPAIR any concerns found in the visual inspection. RERUN «Quick Test».
No, GO to «H31».
32) Check for voltage at HO2S Heater wiring harness connector. Turn ignition off. Disconnect suspect HO2S. Inspect wiring harness for damage and repair as necessary. Turn ignition on. Measure voltage between SIG RTN and VPWR terminal at HO2S wiring harness connector. If voltage is 10.5 volts or less, go to next step. If voltage is more than 10.5 volts, go to step 34)
34)Turn ignition off. With Suspect sensor disconnected, measure resistance between HO2S HEATER GND terminal adn VPWR terminal at HO2S wiring harness connector. If resistance is 3-30 ohms, go to next step, If resistance is not 3-30 ohms, replace HO2S sensor and repeat. I continued to the next step.
35)Leave ignition off and suspect sensor disconnected. Measure resistance between HO2S HEATER GND terminal at HO2S wiring harness connector and HO2S case. Measure resistance between HO2S HEATER GND terminal and SIG RTN terminall at HO2S wiring harness connector. Measure resistance between VPWR terminal at HO2S wiring harness connector and HO2S case. If each resistance measurement is more than 10,000 ohms, go to next step. If any resistance is 10,000 or less, replace HO2S and repeat. Thats the step where I metered all open lines, but i may have metered the wrong side of the HO2S wiring harness.
36)Check for short circuit. Leave igniton off and sensor disconnected. Disconnect scan tester from DLC (if applicable). Disconnect PCM 104-pin connector. Inspect connector for damage and replace is necessary.
Install EEC-V breakout box (014-009050), leaving pcm disconnected. Measure resistance between suspect sensor and test pins indicated as follows:
MIESK5 NOTE, instead of breakout box, go to the PCM CONNECTOR pin instead;
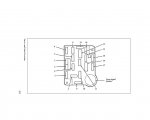
PIN LEGEND
Pin Number Circuit Circuit Function
1 315 (P/O) PCM to Transmission Shift Solenoid No. 2
2 658 (P/LG) PCM to Check Engine Indicator Lamp
3 � Not Used
4 � Not Used
5 � Not Used
6 651 (BK/Y) Dedicated Ground
7 � Not Used
8 � Not Used
9 � Not Used
10 � Not Used
11 � Not Used
12 � Not Used
13 107 (P) PCM Flash EEPROM Power Supply
14 784 (LB/BK) 4x4 Low Range Switch to PCM Indicator Lamp
15 915 (PK/LB) J1850 Bus Negative/Data Negative (Return) to PCM
16 914 (T/O) J1850 Bus Positive/Data Positive
17 � Not Used
18 � Not Used
19 � Not Used
20 � Not Used
21 � Not Used
22 � Not Used
23 259 (O/R) Dedicated Ground to TFI Module
24 570 (BK/W) Dedicated Ground � PCM
25 875 (BK/LB) Ground Logic Module
26 � Not Used
27 237 (O/Y) PCM to Transmission Shift Solenoid No. 1
28 � Not Used
29 224 (T/W) Transmission Overdrive Cancel Switch to PCM
30 � Not Used
31 � Not Used
32 � Not Used
33 676 (PK/O) Vehicle Speed Sensor � Negative (Return) to PCM
34 � Not Used
35 392 (P/LG) Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor No. 3 to PCM
36 968 (T/LB) Mass Airflow Return
37 923 (O/BK) Transmission Oil Temperature to PCM
38 354 (LG/R) Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor to PCM
39 743 (GY) Air Charge Temperature Sensor to PCM
40 238 (DG/Y) Fuel Pump Monitor to PCM/Fuel Pump Relay to Safety Switch
41 198 (DG/O) A/C Pressure Switch to Control Relay
42 � Not Used
43 � Not Used
44 200 (BR) PCM to Air Management No. 2 (Was TAD)
45 � Not Used
46 � Not Used
47 360 (BR/PK) PCM to Electronic Vacuum Regulator � Constant Current
48 382 (Y/BK) PCM to Test Connector No. 2
49 395 (GY/O) Profile Ignition Pickup to PCM
50 929 (PK) PCM to Spark Angle Pulse Width/Spark Output
51 570 (BK/W) Dedicated Ground � PCM
52 � Not Used
53 924 (BR/O) PCM to Transmission Coast Clutch Solenoid
54 480 (P/Y) PCM to Transmission Converter Clutch Control
55 37 (Y) Battery to Load
56 191 (LG/BK) PCM Top Vapor Management Valve � Constant Current
57 310 (Y/R) Knock Sensor No. 1 to PCM
58 679 (GY/BK) Vehicle Speed Sensor � Positive to PCM
59 917 (DG/LG) Misfire Detection Sensor � Feed
60 74 (GY/LB) Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor No. 1 to PCM
61 � Not Used
62 � Not Used
63 � Not Used
64 199 (LB/Y) Manual Lever Position Sensor to PCM
65 352 (BR/LG) Delta Exhaust Pressure Transducer to PCM
66 � Not Used
67 � Not Used
68 � Not Used
69 � Not Used
70 190 (W/O) PCM to Air Management No. 1 (Was TAB)
71 361 ® Power Output from PCM Relay
72 561 (T/R) PCM to Fuel Injector No. 7 Cylinder
73 559 (T/BK) PCM to Fuel Injector No. 5 Cylinder
74 557 (W) PCM to Fuel Injector No. 3 Cylinder
75 555 (T) PCM to Fuel Injector No. 1 Cylinder or Bank No. 1
76 570 (BK/W) Dedicated Ground � PCM
77 570 (BK/W) Dedicated Ground � PCM
78 � Not Used
79 911 (W/LG) PCM to Output Circuit Indicator Lamp/Overdrive Cancel Indicator
80 926 (LG/O) PCM to Fuel Pump Relay Control
81 925 (W/Y) PCM to Electronic Pressure Control No. 1
82 � Not Used
83 264 (W/LB) PCM to Idle Speed Control Motor No. 1
84 136 (DB/Y) Output Shaft Speed to PCM
85 � Not Used
86 � Not Used
87 94 (R/BK) Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor No. 2 to PCM
88 967 (LB/R) Mass Air Flow Sensor to PCM
89 355 (GY/W) Throttle Position Sensor to PCM/Diesel Fuel Injector Pump Lever Sensor
90 351 (BR/W) Power to Engine Sensors
91 359 (GY/R) Sensor Signal Return
92 511 (LG) Stoplamp (Brake On/Off) Switch to Stoplamps
93 387 (R/W) HEGO Sensor Heater Voltage Monitor No. 1 to PCM
94 388 (Y/LB) HEGO Sensor Heater Voltage Monitor No. 2 to PCM
95 389 (W/BK) HEGO Sensor Heater Voltage Monitor No. 3 to PCM
96 � Not Used
97 361 ® Power Output from PCM Relay
98 562 (LB) PCM to Fuel Injector No. 8 Cylinder
99 560 (LG/O) PCM to Fuel Injector No. 6 Cylinder
100 558 (BR/LB) PCM to Fuel Injector No. 4 Cylinder
101 556 (W) PCM to Fuel Injector No. 2 Cylinder or Bank No. 2
102 � Not Used
103 570 (BK/W) Dedicated Ground � PCM
104 � Not Used
DTC P0155 (LR), Test pin No. 94 and test pins No. 24, 76, 91, 97, and 103. If resistance is more than 10,000 ohms, go to next step. If resistance is 10,000 ohms or less, repair short in circuit and repeat..." Source: by Fishallot & 96broncoman
===
P0171 - System Too Lean (Bank 1) The Adaptive Fuel Strategy Fuel System:
continuously monitors fuel delivery
hardware. The code is set when the •Contaminated fuel injectors
adaptive fuel tables reach a rich •Low fuel pressure or running out of fuel
calibrated limit. (fuel pump, filter, fuel supply line
restrictions)
•Vapor recovery system (VMV)
Induction System:
•MAF contamination
•Air leaks between the MAF and throttle
body
•Vacuum leaks
•PCV system concern
•Improperly seated engine oil dipstick
EGR System:
•Leaking gasket
•Stuck EGR valve
•Leaking diaphragm or EVR
Base Engine:
•Exhaust leaks before or near the HO2S
•Secondary air concern
Powertrain Control System:
•PCM concern
MAF Contamination TSB 98-23-10 by Ford for 94-96
MIESK5 NOTE; Tests require high-end scan tool;
here are excerpts;
ISSUE: This TSB article is a diagnostic procedure to address vehicles that exhibit lean driveability symptoms and may or may not have any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) stored in memory.
ACTION: Follow the diagnostic procedures described in the following Service Tip. The revised diagnostic procedure is a more accurate means of diagnosing the symptoms.
SERVICE TIP MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) DISCUSSION
MAF sensors can get contaminated from a variety of sources: dirt, oil, silicon, spider webs, potting compound from the sensor itself, etc. When a MAF sensor gets contaminated, it skews the transfer function such that the sensor over-estimates air flow at idle (causes the fuel system to go rich) and under-estimates air flow at high air flows (causes fuel system to go lean). This means Long Term Fuel Trims will learn lean (negative) corrections at idle and learn rich (positive) corrections at higher air flows.
If vehicle is driven at Wide Open Throttle (WOT) or high loads, the fuel system normally goes open loop rich to provide maximum power. If the MAF sensor is contaminated, the fuel system will actually be lean because of under-estimated air flow. During open loop fuel operation, the vehicle applies Long Term Fuel Trim corrections that have been learned during closed loop operation. These corrections are often lean corrections learned at lower air flows. This combination of under-estimated air flow and lean fuel trim corrections can result in spark knock/detonation and lack of power concerns at WOT and high loads.
One of the indicators for diagnosing this condition is barometric pressure. Barometric pressure (BARO) is inferred by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) software at part throttle and WOT (
there is no actual BARO sensor on MAF-equipped vehicles, except for the 3.8L Supercharged engine). At high air flows, a contaminated MAF sensor will under-estimate air flow coming into the engine, hence the PCM infers that the vehicle is operating at a higher altitude. The BARO reading is stored in Keep Alive Memory (KAM) after it is updated. Other indicators are Long Term Fuel Trim and MAF voltage at idle.
NOTE: THE FOLLOWING PROCEDURE MAY ALSO BE USED TO DIAGNOSE VEHICLES THAT DO NOT HAVE FUEL SYSTEM/HO2S SENSOR DTCs.
Symptoms
Lack of Power
Spark Knock/Detonation
Buck/****
Hesitation/Surge on Acceleration
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Illuminated - DTCs P0171, P0172, P0174, P0175 may be stored in memory
OBDII DTCs
P0171, P0174 (Fuel system lean, Bank 1 or 2)
P0172, P0175 (Fuel system rich, Bank 1 or 2)
P1130, P1131, P1132, (HO2S11 lack of switching, Bank 1)
P1150, P1151, P1152, (HO2S21 lack of switching, Bank 2)
OBDI DTCs
181, 189 (Fuel system lean, Bank 1 or 2)
179, 188 (Fuel system rich, Bank 1 or 2)
171, 172, 173 (HO2S11 lack of switching, Bank 1)
175, 176, 177 (HO2S21 lack of switching, Bank 2)
184, 185 (MAF higher/lower than expected)
186, 187 (Injector pulse width higher/lower than expected)
NOTE: DO NOT DISCONNECT THE BATTERY. IT WILL ERASE KEEP ALIVE MEMORY AND RESET LONG TERM FUEL TRIM AND BARO TO THEIR STARTING/BASE VALUES. THE BARO PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION DISPLAY (PID) IS USED FOR THIS DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE. ALL OBDII APPLICATIONS HAVE THIS PID AVAILABLE. THERE ARE SOME OBDI VEHICLES THAT DO NOT HAVE THE BARO PID, FOR THESE VEHICLES OMIT THE BARO CHECK AND REFER ONLY TO STEPS 2, 3, AND 4 IN THE DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE.
1. Look at the BARO PID. Refer to the Barometric Pressure Reference Chart in this article. At sea level, BARO should read about 159 Hz (29.91 in. Hg). As a reference, Denver, Colorado at 1524 meters (5000 ft.) altitude should be about 144 Hz (24.88 in. Hg.). Normal learned BARO variability is up to ±6 Hz (±2 in. Hg.). If BARO indicates a higher altitude than you are at (7 or more Hz lower than expected), you may have MAF contamination. If available, Service Bay Diagnostic System (SBDS) has a Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor that can be used as a barometric pressure reference. Use "MAP/BARO" test under "Powertrain," "Testers and Meters." Ignore the hookup screen. Connect GP2 to the reference MAP on the following screen.
NOTE: REMEMBER THAT MOST WEATHER SERVICES REPORT A LOCAL BAROMETRIC PRESSURE THAT HAS BEEN CORRECTED TO SEA LEVEL. THE BARO PID, ON THE OTHER HAND, REPORTS THE ACTUAL BAROMETRIC PRESSURE FOR THE ALTITUDE THE VEHICLE IS BEING OPERATED IN. LOCAL WEATHER CONDITIONS (HIGH AND LOW PRESSURE AREAS) WILL CHANGE THE LOCAL BAROMETRIC PRESSURE BY SEVERAL INCHES OF MERCURY (±3 Hz, ±1 in. Hg.).
NOTE: BARO IS UPDATED ONLY WHEN THE VEHICLE IS AT HIGH THROTTLE OPENINGS. THEREFORE, A VEHICLE WHICH IS DRIVEN DOWN FROM A HIGHER ALTITUDE MAY NOT HAVE HAD AN OPPORTUNITY TO UPDATE THE BARO VALUE IN KAM. IF YOU ARE NOT CONFIDENT THAT BARO HAS BEEN UPDATED, PERFORM THREE OR FOUR HEAVY, SUSTAINED ACCELERATIONS AT GREATER THAN HALF-THROTTLE TO ALLOW BARO TO UPDATE.
2. On a fully warmed up engine, look at Long Term Fuel Trim at idle, in Neutral, A/C off, (LONGFT1 and/or LONGFT2 PIDs). If it is more negative than -12%, the fuel system has learned lean corrections which may be due to the MAF sensor over-estimating air flow at idle. Note that both Banks 1 and 2 will exhibit negative corrections for 2-bank system. If only one bank of a 2-bank system has negative corrections, the MAF sensor is probably not contaminated.
3. On a fully warmed up engine, look at MAF voltage at idle, in Neutral, A/C off (MAF V PID). If it's 30% greater than the nominal MAF V voltage listed in the Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis (PC/ED) Diagnostic Value Reference Charts for your vehicle, or greater than 1.1 volts as a rough guide, the MAF sensor is over-estimating air flow at idle.
4. If at least two of the previous three steps are true, proceed to disconnect the MAF sensor connector. This puts the vehicle into Failure Mode and Effects Management (FMEM). In FMEM mode, air flow is inferred by using rpm and throttle position instead of reading the MAF sensor. (In addition, the BARO value is reset to a base/unlearned value.) If the lean driveability symptoms go away, the MAF sensor is probably contaminated and should be replaced. If the lean driveability symptoms do not go away, go to the PC/ED Service Manual for the appropriate diagnostics.
NOTE:
DUE TO INCREASINGLY STRINGENT EMISSION/OBDII REQUIREMENTS, IT IS POSSIBLE FOR SOME VEHICLES WITH MAF SENSOR CONTAMINATION TO SET FUEL SYSTEM DTCs AND ILLUMINATE THE MIL WITH NO DRIVEABILITY CONCERNS. DISCONNECTING THE MAF ON THESE VEHICLES WILL, THEREFORE, PRODUCE NO IMPROVEMENTS IN DRIVEABILITY. IN THESE CASES, IF THE BARO, LONGFT1, LONGFT2, AND MAF V PIDs INDICATE THAT THE MAF IS CONTAMINATED, PROCEED TO REPLACE THE MAF SENSOR.
After replacing the MAF sensor, disconnect the vehicle battery (5 minutes, minimum) to reset KAM, or on newer vehicles, use the "KAM Reset" feature on the New Generation Star (NGS) Tester and verify that the lean driveability symptoms are gone.
---------
--
See this for more info such as abbreviations, acronyms, terms and code Possible Causes (= to above)HO2S (Heated Oxygen Sensor), Service Tips TSB 01-9-7 for 96 Bronco
-----
Fuse Block Diagram in a 96
Fuse Protection Amps Circuits Protected
1 30 Heater/A/C Blower
2 30 Wiper/Washer
3 3A Idle Switch (Diesel Only)
4 15 Warning Buzzer/Chime Module, Exterior Lamps, Instrument Illumination, Trailer Exterior Lamp Relay
5 10 Air Bag Restraint
6 15 A/C Clutch, Diesel Aux. Fuel Selector a, Remote Keyless Entry
7 15 Turn Lamps, Rear Window Defrost a
8 15 Courtesy/Dome/Cargo Lamps, Electric Outside Mirrors, Speedometer Memory, Warning Buzzer/Chime Module, Overhead Console (Bronco) Sun Visor Illumination (Bronco)
9 25 Power Point
10 4 Instrument Illumination
11 15 Radio, Radio Display Dim
12 20 C.B. Power Door Locks, Electronic Shift Motor 4WD, Power Lumbar, Tailgate Power Window, Key Switch a, Power Driver Seat (SuperCab Only)
13 15 Stop/Hazard Lamps, Anti-Lock Brake Module Memory Power (F-Series Only), Speed Control, Stop Sense for: Powertrain Control, Anti-Lock Brakes, Automatic Transmission Shift Interlock
14 20 C.B. Power Windows, Tailgate Power Window, Instrument Panel Switch a
15 20 Anti-Lock Brakes (F-Series Only)
16 15 Cigar Lighter, Data Link Connector
17 10 Warning Buzzer/Chime Module, Warning Indicators, Diesel Indicators a, Gauges, Tachometer, Transmission Control Switch
18 10 Electronic Shift Module 4WD, Speedometer, Air Bag Restraint, Automatic Transmission Shift Interlock, Automatic Day/Night Mirror Overhead Console (Bronco), APCM (Diesel)
-
for more info on Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) or Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor (HEGO) Old Acronym), see my site @
http://www.broncolinks.com/index.php?index=149
Connector Pin-Out Diagram in a 96 w/Nomenclature
Source: by HardMaple at Ford Bronco Zone Forums
http://broncozone.com/topic/15022-o2-sensor-question/page__st__20__start__20
He also gives pin-point tests for;
For P0141:
"1) Visually inspect the circuit. Make sure the wire is not sitting on the exhaust and burnt through. Check fittings for loose pins or corrosion. Make sure you actually check these things, my tailgate motor problem was caused by a corroded connector and I just replace a wire in my IAC circuit today because of a hidden wire break.
2) Key off. Disconnect O2 Sensor wiring harness. Key on, engine off. Measure voltage between VPWR and Sig Ret at the harness. If its greater than 10.5V - move to step 3. If less than 10.5V - make sure battery voltage is greater than 10.5V. Then Key off. Disconnect battery. Disconnect PCM harness. Check resistance between Pin 71 and VPWR at the sensor harness, and between Pin 97 and VPWR at the sensor harness. If the resistance is greater than 4.0 ohms, check fuse and then repair circuit. If resistance is 4.0 ohms or less, move to step 3.
3) If voltage in step 2 is greater than 10.5V or resistance 4.0 ohms or less, Key off - O2 harness disconnected. Measure resistance between HTR GRD and VPWR on the sensor side of the harness. If resistance is between 3 and 30 ohms, go to step 4. If resistance is less than 3 ohms or greater than 30 ohms, replace O2 sensor.
4) Measure resistance between GRD at sensor harness and the sensor case. Measure resistance between GRD terminal at sensor harness and Signal Return terminal. Measure resistance between VPWR terminal and sensor housing. If any of these are below 10K ohms, replace the 02 sensor. If all 3 tests are 10K ohms or more, move to step 5.
5) Key off, PCM disconnected, sensor harness disconnected. Test resistance between Pin 95 at the PCM harness (sensor side of the harness) and the following: Pins 24, 76, 103, 91, and 97. If the resistance is less than 10K ohms, repair the shorted circuit. If all resistances are greater than 10K ohms, move to step 6.
6) Key off, sensor disconnected, PCM disconnected. Check resistance between Pin 95 and GRD pin at the sensor harness. If resistance is less than 4.0 ohms, repeat all tests and then replace PCM if tests confirm this. If resistance is greater than 4.0 ohms, repair the circuit.
((BTW, I take no responsibility for you replacing the PCM as I did not perform the tests myself.))"

